One part of the business world that often catches new owners by surprise is the importance of legal compliance. There’s a few reasons for this. First, the act of doing business seems relatively straightforward. Purchase or manufacture your products, then sell them to consumers for a profit. But legal parameters demand that all companies operate under a certain M.O. Some of these are to protect the business, others the consumer. One example of this is GDPR compliance.
Legislation acts on many different levels. Sometimes, it’s local, and other times, like the GDPR, it’s a federal mandate. The GDPR, in particular, gives many new businesses trouble. So, What is the GDPR? Why is GDPR compliance so important? How does GDPR compliance affect businesses?
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, if you’re wondering: is inFlow GDPR compliant? Yes! inFlow is GDPR compliant. If you’re looking for more specifics, you can read our privacy policy.
What is the GDPR?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. In simple terms, the GDPR is a collection of European laws that apply to any and all businesses that operate within the European sphere. These laws impose certain restrictions on the way that companies handle customer data.
These regulations protect citizen’s privacy, and Europe as a whole takes them very, very seriously. For example, in 2021, a European watchdog hit Amazon with a whopping $887 million fine. And despite that jaw-dropping amount, it was quickly surpassed by Meta in 2023, who had to pay an eye-watering $1.3 billion for violating GDPR laws related to data transfers.
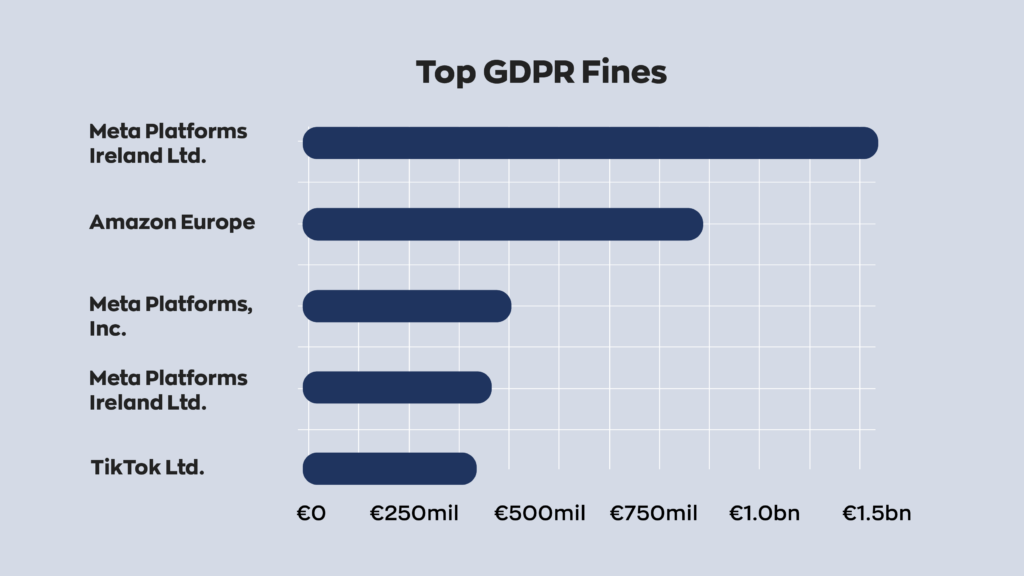
The chances of your business ever being fined that much are really, really slim. At the same time, it serves as a cautionary tale: remain compliant or pay the price.
What is GDPR compliance?
GDPR compliance just means that your business operates within GDPR regulations. As we mentioned before, most of these regulations stipulate certain rules regarding customer data. And it’s really important that you take it seriously.
We already touched on the giant Amazon fee, but it’s essential to understand the surrounding context. Before that, Google held the record for the largest GDPR fee– at a comparatively measly $65 million. That’s nearly a fifteen-fold increase.
And being a non-European citizen doesn’t mean you’re free from its rules, either.
Does the GDPR affect businesses outside of Europe?
Yes. The big thing about the GDPR is that it affects any business that operates within Europe, regardless of its home country. If you sell and ship to Europe, you must be GDPR compliant. There’s no way around it. You can choose not to do business in Europe if you really want to avoid it, but that means giving up a huge market. And a lot of profit along with that.
What are GDPR requirements?
The most important part of GDPR is the data subject rights that it grants to individuals. These rights all have a common theme: they exist to give individuals control over their personal data. Here’s a brief explanation of all of them.

Right to be informed
This data right states that data subjects (individuals using the relevant service) have the right to know what data the organization is collecting. This extends to informing data subjects about how long you plan to store their data, who else will see it, and how they can file a complaint.
Right of access
Data subjects have the right to submit access requests. This means they can request (and subsequently obtain) information about the status of their data. Whether the organization is processing it, and so on. The GDPR stipulates that the organization is required to provide a copy of personal data, along with additional information.
Right to rectification
This right specifically addresses inaccurate collected information. If the organization collects incorrect information, the relevant data subject can request them to update this data. This isn’t particularly difficult, but the GDPR imposes a strict deadline. If the organization confirms they have incorrect data, they have one month to rectify it.
This is likely the most challenging regulation to comply with. Depending on storage methods, altering one data set can affect the entire database.
Right to restrict processing
Under certain conditions, a data subject can request that the data holder limit their use of relevant information. Once data becomes restricted, the data holder is legally unable to process that data without the subject’s consent.
Right to erasure
As the name suggests, the right to erasure allows the individual to ask you to remove their data. There are certain conditions that must be met if a business is to delete information. Additionally, there are many cases where the data holder can legally decline the request.
Right to object to processing
This rule mainly targets the use of consumer data for marketing campaigns. Data subjects can, at any time, request that their information not be used for marketing purposes. While this rule is simple, Europe also enforces it stringently.
Right to automated decision-making and profiling
This is another rule that GDPR compliance agencies strictly regulate. This law dictates certain rules for data holders that autonomously process data. It states that data subjects have the right to avoid autonomous processing if it produces a legal effect.
Right to data portability
This regulation is a bit outdated. It stipulates that data subjects have the right to receive data in a cohesive and machine-readable format. Nowadays, that’s easy– everyone has a computer in their pockets at all times. Back then, it was more important. That said, it still plays an important role today. It keeps data holders from presenting information in such a way that it becomes useless.

Why is GDPR compliance necessary when thinking of software?
The concept can be tricky to wrap your head around, but the modern world runs on data. It dictates marketing strategies and decision-making on a global scale. Data is one of the most valuable resources there is. And it’s a resource that businesses can collect easily. GDPR compliance is a way to regulate the way companies are collecting that resource.
The bottom line is if you’re going to do business in the EU, you’ll need to ensure you’re following the rules, and being GDPR compliant is a part of that. This means being thoughtful about the software you choose.
That’s why we made sure we at inFlow were following GDPR compliance to give our customers peace of mind. But just because we’re GDPR compliant doesn’t mean everyone is, so be sure to do your due diligence when choosing your tech stack.






0 Comments